Zubní nerv: Co to je, proč bolí a co s tím dělat
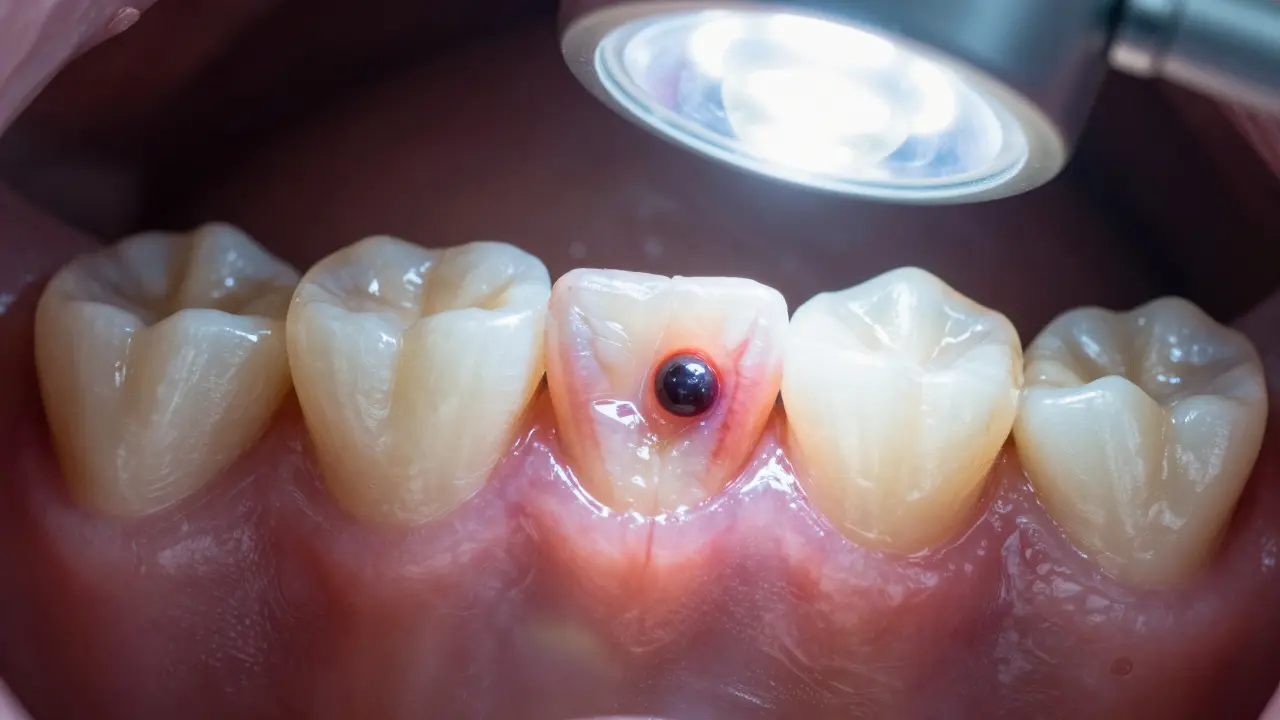
When you feel a sharp, throbbing pain in your tooth, it’s often not just the tooth itself—it’s the zubní nerv, vnitřní nervový a cévní systém zubu, který reaguje na infekci, poškození nebo tlak. Also known as pulpa, it’s the living core of your tooth, and when it gets inflamed, the pain doesn’t just fade away with painkillers. Many people think a toothache is just a minor annoyance, but a swollen or infected zubní nerv can lead to serious complications, including abscesses, bone loss, or even spreading infection.
What triggers this pain? Usually, it’s zubní kazy, prohlubující se rozklad skloviny a dentinu, který nakonec dorazí k nervu. But it can also be caused by a cracked tooth, a loose filling, or even bruxism—grinding your teeth at night. The nerve doesn’t have room to swell, so pressure builds up fast. That’s why the pain often gets worse when you lie down, bite down, or drink something hot or cold. It’s not just sensitivity—it’s a warning sign your body can’t ignore.
Some think they can wait it out, or use home remedies to numb the pain. But if the nerve is infected, antibiotics won’t fix it. The infection needs to be drained and the nerve removed—this is root canal treatment. Delaying it only makes the procedure harder, more expensive, and risks losing the tooth entirely. You don’t need to suffer silently. If you’ve had pain for more than a day or two, especially if it wakes you up at night, it’s time to see a dentist.
The good news? Modern dentistry can save almost every tooth with an infected nerve. Root canal therapy is routine, painless thanks to anesthesia, and lets you keep your natural tooth for decades. It’s far better than extraction, which leads to shifting teeth, bite problems, and eventually, more expensive replacements.
In the articles below, you’ll find real-life stories and clear advice about what happens when the zubní nerv gets damaged—how to recognize the early signs, what treatments actually work, and why skipping the dentist only makes things worse. You’ll also learn how to prevent nerve damage before it starts, whether you wear braces, have fillings, or just use a toothbrush every day. These aren’t theoretical tips—they’re based on what dentists see every week in their clinics. Don’t wait until the pain becomes unbearable. Know what’s happening inside your tooth—and what to do next.
Kdy je nutná endodoncie? Vše, co potřebujete vědět o léčbě zubních kanálků
Endodoncie je nutná, když je zubní nerv infikovaný. Uzavření kanálků zachraňuje zub před vytažením. Zjistěte, kdy je léčba nezbytná a co se stane, když ji odložíte.
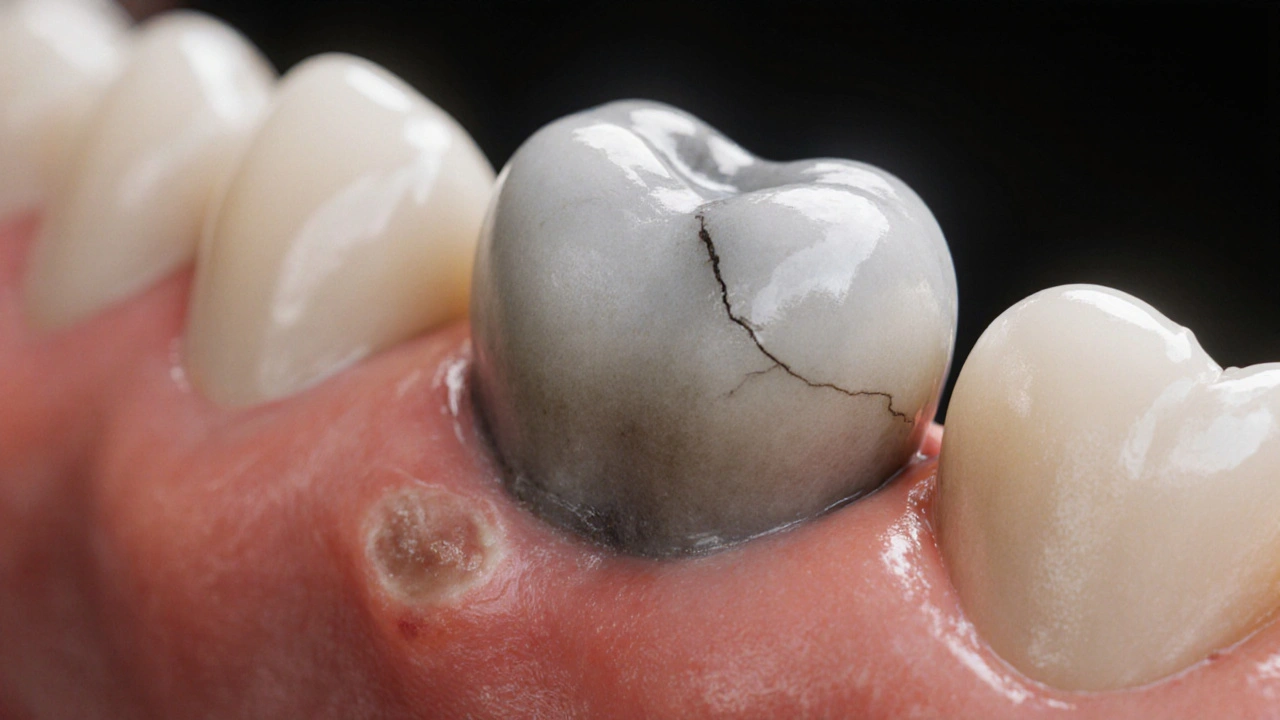
read moreProč je zub mrtvý? Příčiny, příznaky a co dělat, když zub přestal reagovat
Zub může být mrtvý i bez bolesti. Zjistěte, proč to nastává, jak ho poznat a jak ho zachránit, aby se nešířila infekce do těla. Včetně dopadu na keramické zuby.
read more